Welcome to the exciting world of User Experience (UX) design! In this journey, we’ll explore the foundational concepts that aspiring UX enthusiasts need to master.
Imagine you’re the architect of a digital space, and your goal is to create an environment where users feel comfortable, engaged, and satisfied. That’s the essence of UX design.
User Experience is about more than just making things look pretty; it’s about crafting interactions that leave a lasting impression.
In a world filled with digital interfaces, understanding and perfecting UX is the key to creating products and websites that people love to use.
Think of UX as the ABCs of digital design. Before diving into the complexities, it’s crucial to grasp the basics.
These fundamentals serve as the building blocks for your journey to becoming a proficient UX designer.
Table of Contents
Understanding User-Centered Design
Definition and Principles of User-Centered Design
User-Centered Design (UCD) is at the heart of User Experience (UX). It’s like tailoring a suit – not based on what you find stylish, but on what the person wearing it feels comfortable in.
In UCD, the user takes center stage. Principles like simplicity, consistency, and feedback guide us in creating designs that resonate with the user.
The Role of Empathy in Designing for User Needs and Preferences
Empathy is our compass in User Experience (UX). It involves putting ourselves in the user’s shoes, understanding their frustrations, and celebrating their successes.
By empathizing with users, we design solutions that genuinely meet their needs.
It’s not just about features; it’s about solving real-life problems for real people. So, as you continue on your user experience (UX) journey, always keep empathy in your toolkit.
No. 1 Usability Principles
Definition and Importance of Usability in UX
Usability is the measure of how easily users can interact with a product. It’s like ensuring a book is easy to read rather than deciphering a cryptic code.
In UX, usability is non-negotiable. If users struggle to navigate, understand, or enjoy an interface, it’s a sign that usability needs attention.
Key Usability Principles for Creating Intuitive Interfaces
Picture a door with a handle – you instinctively know how to use it because of its usability.
Similarly, in UX, we follow principles like consistency, simplicity, and feedback to create interfaces that users can effortlessly understand.
These principles are the secret sauce to crafting designs that feel intuitive and natural, leading to a delightful user experience.
Practical Tips to Apply Usability Principles:
- User Testing Protocols: Incorporate regular usability testing sessions into your design process. Observe how users interact with your prototypes and gather feedback to identify pain points and areas for improvement.
- Consistency Across Platforms: Maintain a consistent design language and interface elements across different platforms (web, mobile, etc.). Users should feel a seamless transition between devices, enhancing usability.
- Accessibility Checks: Regularly audit your designs for accessibility. Ensure that your interfaces are usable by individuals with diverse abilities. Test for color contrast, text readability, and screen reader compatibility to create an inclusive user experience.
No. 2 Information Architecture
Importance of Organizing and Structuring Information
Imagine a library where books are randomly scattered with no order. Chaotic, right? Information Architecture (IA) is like the Dewey Decimal System for digital spaces.
It’s about organizing and structuring information so that users can find what they need without getting lost. A well-designed IA is the roadmap that ensures users reach their destination seamlessly.
Creating Effective Navigation Systems for Seamless User Journeys
Navigation in UX is akin to road signs. A clear path with signposts helps users navigate effortlessly.
Whether it’s a website or an app, a well-thought-out navigation system ensures users can move through the interface with ease.
It’s about guiding them on a smooth journey, minimizing confusion, and maximizing satisfaction.
Practical Tips for Information Architecture:
- Card Sorting for Content Organization: Conduct card sorting sessions with users to understand how they naturally categorize information. Use these insights to organize content logically, making it easier for users to navigate.
- Clear Navigation Labels: Choose clear and concise labels for navigation menus and categories. Avoid jargon or overly creative terms; clarity is key. Users should intuitively understand where each link leads.
- Hierarchical Structure for Complex Information: If dealing with complex information, implement a hierarchical structure. Break down content into categories, subcategories, and pages, guiding users through a logical flow and preventing information overload.
No. 3 Interaction Design
Basics of Interaction Design and Its Impact on User Engagement
Interaction Design is where digital products come to life. It’s the difference between watching a movie and being part of one.
In user experience (UX), we focus on creating meaningful interactions between users and the interface. Every click, swipe, or tap should serve a purpose, engaging users and making the experience enjoyable.
Incorporating Feedback and Responsiveness for a Dynamic User Experience
Think of a responsive website like a conversation – it listens and adapts. User feedback is our compass for improvement.
By incorporating feedback and ensuring responsiveness, we create a dynamic user experience (UX) that evolves based on user needs.
It’s about constant refinement, making the user experience a two-way street of communication and enhancement.
Practical Tips for Interaction Design:
- Define Clear User Paths: Map out the user journey and define clear paths for users to accomplish tasks. Ensure that interactions guide users logically from one step to the next, minimizing confusion.
- Feedback for User Actions: Implement immediate and informative feedback for user actions. Whether it’s a button click or form submission, users should receive visual or auditory cues confirming their actions, providing a sense of control and understanding.
- Progressive Disclosure: Present information progressively, revealing details as users need them. Avoid overwhelming users with too much information upfront. This approach keeps interfaces clean and user-focused, revealing complexity gradually.
No. 4 Visual Hierarchy
Significance of Visual Hierarchy in Guiding User Attention
Visual Hierarchy is like a traffic light for design, guiding users on where to focus first. It’s not just about aesthetics; it’s about creating a natural flow of information.
Elements like size, color, and placement are strategically used to direct attention.
Just as headlines grab your eye in an article, visual hierarchy ensures users catch the most critical information at a glance.
Choosing and Implementing Effective Typography for Readability and Aesthetics
Typography is the unsung hero of User Experience (UX). Imagine reading a book with tiny, illegible text – frustrating, right?
In UX, selecting the right fonts and sizes is crucial. It’s not just about readability; it also adds personality to the design.
Effective typography enhances the overall user experience, making the content not only easy to read but also visually appealing.
Practical Tips for Visual Hierarchy:
- Prioritize Key Information: Arrange elements on the page based on importance. Use size, color, and contrast to emphasize critical information, guiding users’ attention to key elements first.
- Logical Flow in Design: Create a natural flow in the design by arranging content in a way that mirrors the user’s expected reading pattern. This ensures a seamless and intuitive visual experience.
- Consistent Element Styling: Maintain consistency in styling for similar elements. Whether it’s buttons, headings, or images, a consistent design language helps users understand the significance of each element and reinforces visual hierarchy.
No. 5 Typography in UX Design
Importance of Typography in User Interface Design
Typography in User Experience (UX) design is like choosing the right tone for a conversation – it sets the mood and determines how the message is received.
The fonts we select convey more than just words; they evoke emotions and influence user perception.
Typography is a silent storyteller, subtly guiding users through the interface.
Best Practices for Selecting and Implementing Typography in UX
Just as a well-chosen outfit complements a person’s style, proper typography enhances the design.
Best practices include considering readability, choosing fonts that align with the brand, and maintaining consistency across the interface.
Typography isn’t just about letters; it’s about creating a visual rhythm that harmonizes with the overall user experience.
Practical Tips for Typography in User Experience Design:
- Prioritize Readability: Choose fonts that prioritize readability. Ensure text is easily legible across various devices and screen sizes. Test font sizes and styles to find the optimal balance between aesthetics and readability.
- Hierarchy with Font Styles: Establish a hierarchy using different font styles (e.g., bold, italic) to emphasize varying levels of information. Headings should stand out, guiding users through the content.
- Consistent Font Pairing: Select and pair fonts consistently throughout the interface. Consistency promotes a cohesive design, making it easier for users to associate specific fonts with particular types of content or actions.
No. 6 Prototyping in UX Design
Role and Significance of Prototyping in the Design Process
Prototyping is the dress rehearsal before the big show in UX design. It’s more than just a static blueprint; it’s a dynamic model that brings ideas to life.
Prototypes allow us to test functionality, flow, and user interactions before committing to the final product.
It’s a valuable step that bridges the gap between imagination and reality.
Different Prototyping Tools and Methods for Effective User Testing
Imagine building a sandcastle before constructing a grand sand sculpture. Prototyping tools are our digital shovels and buckets.
From simple paper sketches to interactive digital prototypes, these tools help us iterate and refine designs.
By involving users in testing prototypes, we gather invaluable insights that shape the final product.
It’s not just about what looks good on paper; it’s about creating a design that works seamlessly in the user’s hands.
Practical Tips for Prototyping in User Experience Design:
- Start with Low-Fidelity Prototypes: Begin with low-fidelity prototypes, such as paper sketches or wireframes, to quickly iterate and gather initial feedback. This allows for early testing without investing extensive time in high-detail designs.
- Interactive Elements for Realism: Incorporate interactive elements in your prototypes to mimic real user interactions. This helps users and stakeholders better understand the flow and functionality of the final product.
- Iterate Based on Feedback: Use feedback from prototype testing to iterate and refine your designs. The prototyping phase is an iterative process, and each round of testing provides valuable insights for improvement.
No. 7 Wireframing
Introduction to Wireframing as a Blueprint for UX Design
Wireframing is like sketching the skeleton before adding the flesh and clothes. It’s the blueprint, the basic structure that outlines the placement of elements.
In user experience (UX), wireframes serve as a visual guide, showcasing the skeletal framework of a design.
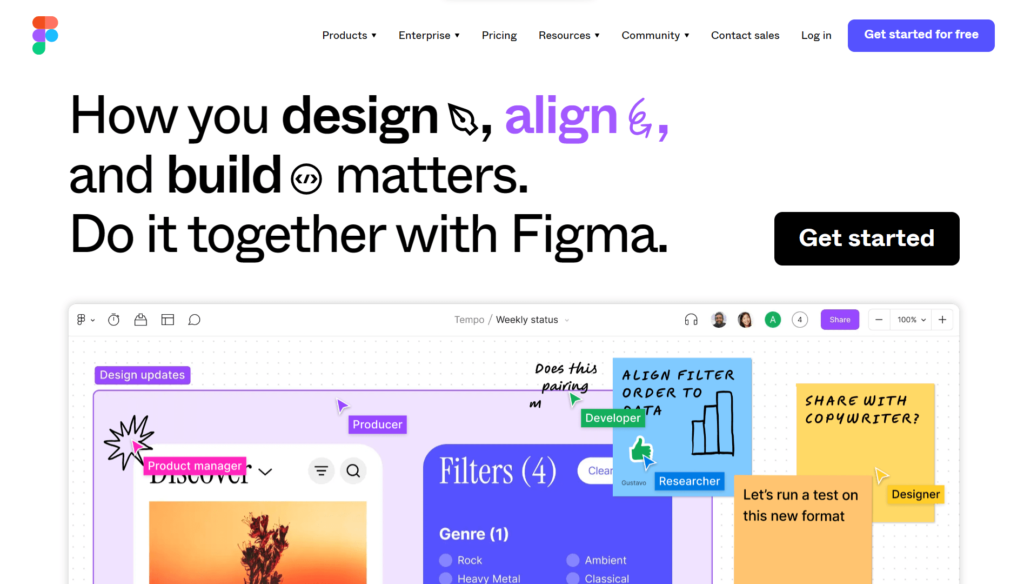
They focus on layout and functionality, providing a clear foundation for the final product.
Best Practices for Creating Wireframes to Communicate Design Concepts
Think of wireframes as the architectural plans for a building. Clarity is key. Best practices involve simplicity, using basic shapes to represent elements, and emphasizing functionality over aesthetics.
By keeping wireframes clean and uncluttered, designers can effectively communicate the design concept without getting bogged down by details.
It’s the first step in turning ideas into tangible, user-friendly experiences.
Practical Tips for Wireframing:
- Focus on Functionality: In wireframes, prioritize functionality over aesthetics. Clearly outline the layout, structure, and interactions without getting into detailed design elements. It’s the blueprint for your design.
- Simplify with Basic Shapes: Use basic shapes to represent elements and maintain a clean and simple appearance. This avoids unnecessary distractions, allowing stakeholders and users to focus on the overall layout and structure.
- Gather Early Feedback: Share your wireframes early in the design process to gather initial feedback. This helps identify any fundamental issues with the layout or user flow before investing time in higher-fidelity designs.
No. 8 User Research Techniques
Importance of User Research in Understanding Target Audiences
User research is the detective work in UX design. It’s about understanding who the users are, what they need, and how they behave.
By diving into the minds of our audience, we gain insights that shape design decisions.
It’s not a guessing game; it’s a deliberate effort to align the design with the preferences and expectations of the intended users.
Conducting Effective User Interviews, Surveys, and Usability Testing
Imagine having a conversation with your users before designing their space. User interviews and surveys are like sitting down for a cup of coffee, getting to know their preferences and pain points.
Usability testing is the hands-on experience – watching how users interact with the design in real-time.
By combining these techniques, designers gather valuable data that guides decision-making and ensures the final product resonates with the intended audience.
User research isn’t just a phase; it’s an ongoing dialogue that informs and refines the design process.
Practical Tips for User Research Techniques:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define your research objectives before starting. Understand what specific insights you aim to gather, whether it’s understanding user needs, preferences, or pain points.
- Mix Quantitative and Qualitative Methods: Combine quantitative methods like surveys with qualitative methods like interviews and usability testing. This comprehensive approach provides a holistic understanding of user behavior.
- Build Personas: Create user personas based on your research findings. Personas humanize your target audience, making it easier to design with specific user needs and behaviors in mind.
No. 9 Accessibility in User Experience Design
Ensuring Inclusivity Through Accessible Design Practices
Accessibility in user experience (UX) is about creating a digital world where everyone, regardless of abilities or disabilities, can participate equally.
It’s the digital equivalent of building ramps for wheelchair access. Inclusive design ensures that all users can access and interact with digital products, fostering a sense of belonging and usability for everyone.
Addressing Common Accessibility Considerations in User Experience
Consider accessibility as the universal language of design. From providing alternative text for images to designing with sufficient color contrast, it’s about considering diverse needs.
By addressing common accessibility considerations, such as keyboard navigation and screen reader compatibility, designers contribute to a more inclusive and user-friendly digital landscape.
In User Experience (UX), the goal is not just to design for some; it’s to design for all.
Practical Tips for Accessibility in User Experience Design:
- Ensure Keyboard Accessibility: Design interfaces that can be navigated using a keyboard alone. This ensures users with motor disabilities or those who rely on assistive technologies can interact seamlessly.
- Provide Alternative Text for Images: Include descriptive alt text for images to assist users with visual impairments. Screen readers rely on alt text to convey the content and context of images.
- Test with Accessibility Tools: Use accessibility tools and conduct regular audits to ensure your designs meet accessibility standards. Tools like screen readers, color contrast checkers, and keyboard testing can uncover potential issues.
No. 10 Data-Driven Decision Making
Utilizing Analytics for Informed Design Decisions
Data is the compass that guides us in the vast sea of user interactions. In UX design, analytics provide insights into user behavior, preferences, and pain points.
By leveraging data, designers make informed decisions rather than relying on gut feelings.
It’s like having a map that helps navigate the design landscape, ensuring that choices are rooted in user realities.
Implementing A/B Testing and Analyzing User Behavior Patterns
A/B testing is the science experiment of user experience (UX). It involves presenting users with different versions of a design and analyzing which performs better.
By experimenting and analyzing user behavior patterns, designers fine-tune the user experience.
It’s not about assumptions; it’s about evidence-based adjustments that optimize the design for user satisfaction and engagement.
In User Experience (UX), data is not just numbers; it’s the key to unlocking a design that truly resonates with the audience.
Practical Tips for Data-Driven Decision Making:
- Define Key Metrics: Clearly define the key metrics aligned with your design goals. Whether it’s conversion rates, user engagement, or task completion, having specific metrics ensures focused data analysis.
- Implement A/B Testing: Use A/B testing to compare variations of your design and identify which performs better. This method provides concrete data on user preferences and behavior.
- Utilize Analytics Tools: Leverage analytics tools to gather user data and behavior patterns. Platforms like Google Analytics offer valuable insights into how users interact with your design, helping you make informed decisions.
Emerging Trends and Future of UX
Overview of Current Industry Trends in UX Design
The world of User Experience (UX) is ever-evolving, and staying ahead means riding the wave of emerging trends.
From voice interfaces to augmented reality, understanding the current landscape is essential.
Trends like dark mode, microinteractions, and personalized experiences are shaping the present and future of UX design.
Preparing for the Future by Staying Updated on Emerging Technologies
Imagine UX design as a constantly updating software – to stay relevant, you need the latest version.
Aspiring UX enthusiasts must keep a finger on the pulse of emerging technologies.
Whether it’s the rise of AI-driven experiences or the integration of immersive technologies, being aware of the latest trends ensures that your designs are not just current but future-proof.
In User Experience (UX), adaptability is the key to longevity.
Practical Tips for Staying Updated on Emerging Trends in UX:
- Subscribe to Industry Newsletters: Stay informed by subscribing to newsletters from reputable UX design platforms and industry leaders. Receive regular updates on emerging trends, technologies, and best practices.
- Attend Virtual Conferences and Webinars: Participate in virtual UX conferences and webinars to hear from experts and gain insights into the latest trends. Engage in discussions and network with professionals in the field.
- Join Online Communities: Become a part of online UX communities on platforms like LinkedIn, Reddit, or specialized forums. Engaging with the community allows you to exchange ideas, share experiences, and stay informed about current discussions and trends.
Conclusion
From user-centered design to embracing emerging trends, you’ve explored the ABCs of creating digital experiences that resonate with users.
The User Experience (UX) principles discussed serve as your compass in creating meaningful and user-centric digital experiences.
Tips for Aspiring UX Enthusiasts:
- Curiosity is Key: Stay curious and never stop learning. User Experience is a field that thrives on exploration and discovery.
- User-Centric Mindset: Always prioritize the needs and experiences of your users. Empathy is at the core of great design.
- Iterate and Refine: Design is an iterative process. Embrace feedback, iterate on your designs, and constantly seek improvement.
- Diversify Skills: While mastering User Experience, consider expanding your skill set. Understanding related areas like graphic design or coding can enhance your capabilities.
- Build a Portfolio: Showcase your projects and document your design process. A well-curated portfolio is a powerful tool in the UX world.
- Network and Collaborate: Connect with fellow UX enthusiasts, join communities, and engage in collaborative projects. Learning from others is invaluable.
- Usability Testing Matters: Regularly conduct usability testing to gain insights into user behavior and refine your designs accordingly.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of industry trends, emerging technologies, and evolving design methodologies. Stay informed to stay relevant.
- Mentorship: Seek guidance from experienced professionals in the field. Mentorship can provide valuable insights and guidance in your journey.
- Passion for Problem-Solving: Approach every design challenge as an opportunity to solve a problem. A passion for problem-solving is the essence of UX design.
Explore Our Learning Resources:
For more beginner-friendly User Experience topics and in-depth insights, be sure to explore our dedicated learning resources page.
Here, you’ll find exclusive content tailored for aspiring UX enthusiasts, including articles, tutorials, and case studies to further enrich your learning experience.
Remember, the path to mastering User Experience is unique for each individual. Your dedication and enthusiasm will propel you forward in creating impactful and user-centered designs. Happy designing, and don’t forget to explore our learning resources for continuous growth!
Happy designing!
Leave a Reply